に行くあなたは楕円のためのパラメータ化方程式を使用して試みることができる任意の角度で回転さ:
x = h + a*cos(t)*cos(phi) - b*sin(t)*sin(phi) [1]
y = k + b*sin(t)*cos(phi) + a*cos(t)*sin(phi) [2]
...ここで、楕円は中心(h、k)の長軸aと半分の軸bを持ち、角度φで回転します。
あなたはその後、勾配= 0のために差別化し、解決することができます
あなたのトンのために多くのソリューションを与える必要があります
0 = dx/dt = -a*sin(t)*cos(phi) - b*cos(t)*sin(phi)
=>
tan(t) = -b*tan(phi)/a [3]
(あなたが興味を持っているそのうちの2つ)、プラグをあなたの最大と最小のxを得るために[1]に戻ります。[2]用
繰り返し:
は(0,0)での楕円を考える= 2:
0 = dy/dt = b*cos(t)*cos(phi) - a*sin(t)*sin(phi)
=>
tan(t) = b*cot(phi)/a [4]
例を試すことができます、b = 1、PI/4回転:
[1] =>
x = 2*cos(t)*cos(PI/4) - sin(t)*sin(PI/4)
[3] =>
tan(t) = -tan(PI/4)/2 = -1/2
=>
t = -0.4636 + n*PI
我々はトンに興味がある= -0.4636とt =
-3.6052は、だから我々が得る:
x = 2*cos(-0.4636)*cos(PI/4) - sin(-0.4636)*sin(PI/4) = 1.5811
と
x = 2*cos(-3.6052)*cos(PI/4) - sin(-3.6052)*sin(PI/4) = -1.5811

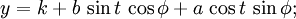
おかげで私の答えを書くために私の年齢を取りました。これは、式2のタイプミスを除いて動作します。マイナス記号はプラスでなければなりません。 –
固定されているので、[2]のtan(t)の解法にも従っているようですが、それも修正しました。うまくいけば、あなたは私のすべてのエラーを見つけた - それはすべてここにエンベロープの裏に書かれている;) –
私は例では、別のエラーがあると思う:xの最初のt値は-0.4636で、2番目の値は-3.6052 (-0.4636 - piに等しい)? – brianmearns